What are PBMCs
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) are a diverse mixture of highly specialized immune cells that play key roles in keeping our bodies healthy. This brief review tells a short story about PBMCs starting with their origin, the different immune cells within the PBMC fraction, isolation of these cells and how to characterize them, and once isolated and characterized, how these cells benefit medical research.
Origin of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
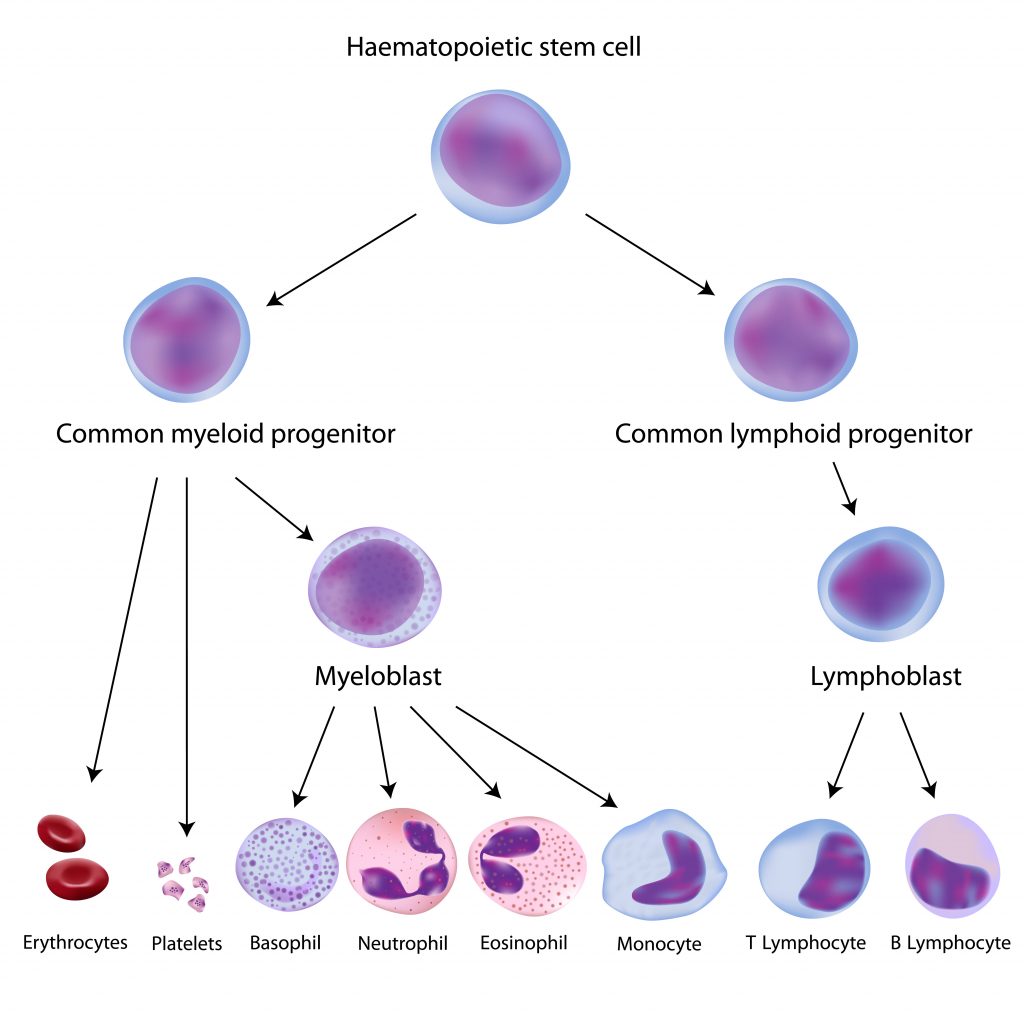
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that reside in the bone marrow. HSCs give rise to all blood cells of the immune system through a process called hematopoiesis. As hematopoietic stem cells progress through hematopoiesis they generate the myeloid (monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, megakaryocytes, dendritic cells, erythrocytes) and lymphoid (T cells, B cells, NK cells) lineages (Figure 1).
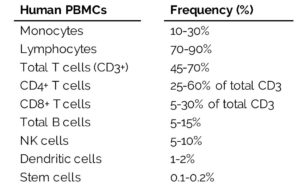
Within both lineages are cells that make up the PBMCs. PBMCs are blood cells with round nuclei that encompass a heterogeneous cell population comprising various frequencies of lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, and NK cells), dendritic cells, and monocytes (Table 1). These cells are critical components of the innate and adaptive immune system which defends the body against viral, bacterial, and parasitic infection and destroys tumor cells and foreign substances.
The Frequency of Different Cell Populations within the PBMC Fraction
Human cell frequencies vary across individuals, but on average, most PBMCs are lymphocytes (70-90%). Lymphocytes play an essential role in cell-mediated and humoral immune responses, primarily associated with the activation of T and B cells.
Within the lymphocyte population, CD3+ T cells contribute to the most significant portion of cells (45-70%). Most T cells exist as resting, naïve T cells, which are T cells that have not been activated by an antigen, or as memory T cells. Activation of naïve T cells occurs through antigen recognition and accounts for a small population of T cells within healthy individuals. Once active, T cells launch a cell-mediated immune response that targets antigens within an infected or diseased cell.
Similarly, CD19+ B cells exist as naïve or memory cells that are awaiting activation by an antigen, and comprise only 5-15% of the total lymphocyte population. Once activated, B cells differentiate into plasma cells capable of secreting antibodies that specifically target free antigens circulating in the bloodstream. The ability to target free antigens by secreted antibodies within the extracellular space is defined as the humoral immune response.
NK cells account for a smaller portion of the lymphocyte population (5-10%) and, from a historical perspective, are part of the innate immune system, our bodies’ front-line defense system. These cells perform their effector function without requiring an antigen and defend the body against tumor activity.
A small portion of white blood cells include dendritic cells (1-2%) that form a critical interface between the innate and adaptive immune system. Dendritic cells, a highly specialized antigen-presenting cell, engulf antigens and present fragments of the antigen to cells of the adaptive immune system eliciting activation of T and B cells.
Varying in complexity and size as compared to lymphocytes, monocytes (10-30%) circulate within the bloodstream to the peripheral tissue where, when stimulated, mature and differentiate into either dendritic cells or macrophages that mediate both the innate and adaptive immune responses by acting as phagocytic and antigen-presenting cells.
Last, but of great importance, are the hematopoietic stem cells. HSCs within the blood and bone marrow give rise to all the cells within the blood, including red blood cells, platelets, lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes. Although desirable for stem cell transplants, this rare cell population accounts for only 0.1-0.2% of the PBMC fraction, making them difficult to isolate from whole blood samples. Injection of mobilizations agents, such as granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) or Plerixafor, can increase the frequency of circulating CD34+ stem cells to o.5-1.5%, allowing for greater quantities of these rare cells from a donor.
Isolation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Two primary techniques that separate peripheral blood mononuclear cells from whole peripheral blood are through the use of a density gradient centrifugation process or by leukapheresis.
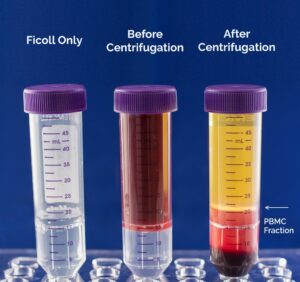
Since cells have a specific density, the use of a density gradient centrifugation process separates the main cell populations, such as lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, and red blood cells, throughout a density gradient medium. For human cells, the medium will have a density of 1.077 g/ml to allow sufficient separation of PBMCs (density < 1.077 g/ml) from red blood cells and granulocytes (density > 1.077 g/ml).1 Layering of whole blood over or under a density medium without mixing of the two layers followed by centrifugation will disperse the cells according to their densities (Figure 2). After centrifugation, the PBMC fraction will appear as a thin white layer at the interface between the plasma and the density gradient medium making it easy to remove the PBMC fraction.
A leukapheresis machine is an automated device that separates the inflow of whole blood from the target PBMC fraction using high-speed centrifugation while returning the outflow material, such as plasma, red blood cells, and granulocytes, back to the donor. On average, leukapheresis provides 14x more PBMCs from a single donor than the density gradient centrifugation process of whole blood (Figure 3). The sheer number of PBMCs within a Leukopak, the product of leukapheresis, makes them ideal for large-scale research studies or pre-clinical trials. Depending on the quality of the leukapheresis machine and the downstream research applications, further processing of a Leukopak may be necessary to remove residual red blood cells (RBC lysis) and granulocytes (density gradient centrifugation).
Figure 2. Whole blood layered onto a density gradient medium. After centrifugation, the PBMC fraction is defined by the white layer at the interface between the plasma and the density gradient medium.
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Research
PBMCs are critical components of the immune system since they can elicit a response to intruders entering the human body and existing cells that have undergone a transformation into a cancerous cell type. Therefore, researchers and clinicians use PBMCs in areas relating to immunology, infectious disease, hematological malignancies, vaccine development, transplant therapy, personalized medicine, and toxicology. Predominately, in vitro PBMC studies provide the most information regarding cell function6, biomarker identification7, and disease modeling8, just to name a few. But the research also expands into in vivo analysis through the use of humanized mice. Reconstitution of immunocompromised mice with human PBMCs allows the study of the human immune system and its response to pathogens, toxins, or cancer in an in vivo model.9
But studies using PBMCs are advancing into more precise human medicine. The generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from single donors PBMC fraction has great implications in personalized medicine regarding disease modeling, drug toxicity screening, drug discovery, and cell replacement therapy.10 And of recent, the use of genome editing technology, such as CRISPR/Cas9, can transform immune cells (T cells from PBMCs) into off-the-shelf CAR-T cells making it possible to treat human cancers without a donor match.11
Conclusion
PBMCs are an important element and a powerful tool for research and clinical studies relating to human health and disease. Through efficient and successful processing and analysis of PBMCs, researchers and clinicians can test immune responses, gain a deeper understanding of the immune system, and apply their findings to treatments and cures for human diseases.
References
Related Services
Our state-of-the-art laboratories process and isolate specific primary cells from human tissue.
Our GMP cell manufacturing facility ensures consistent production and quality standards for cell therapy products.